Home Applications Septentrio The objective is to safeguard the surfac…

With regard to the lunar in situ PNT (positioning, navigation and timing) GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) analogue frequencies and how radio astronomy (RA) can be protected from interference, the following are some key points:
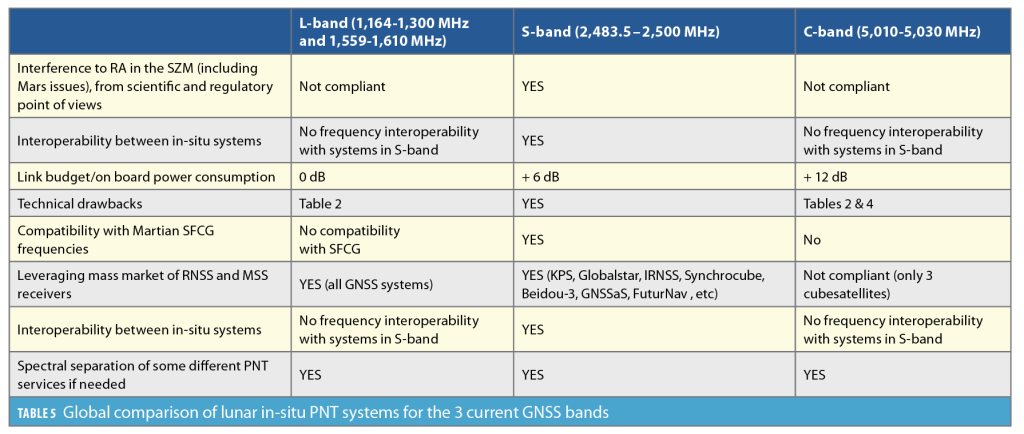
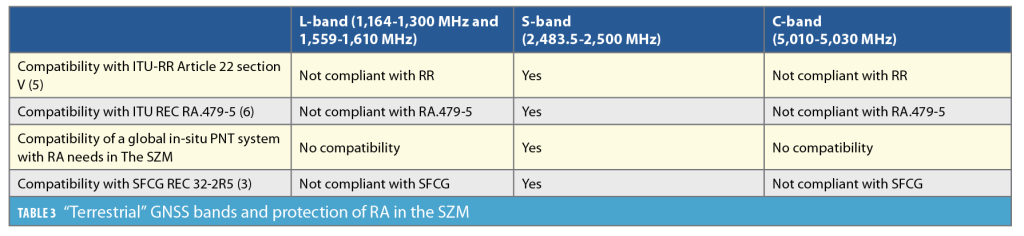
International Telecommunication Union (ITU) regulations: ITU's Radio Regulations and Recommendations exclude L-band Lunar In-Situ-like GNSS systems to protect RAs. the recommendation to use the S-band from 2,483.5 to 2,500 MHz is in line with the Space Frequency Coordination Group (SFCG) and ITU's Radio Regulations and Recommendations for the lunar frequency bands.
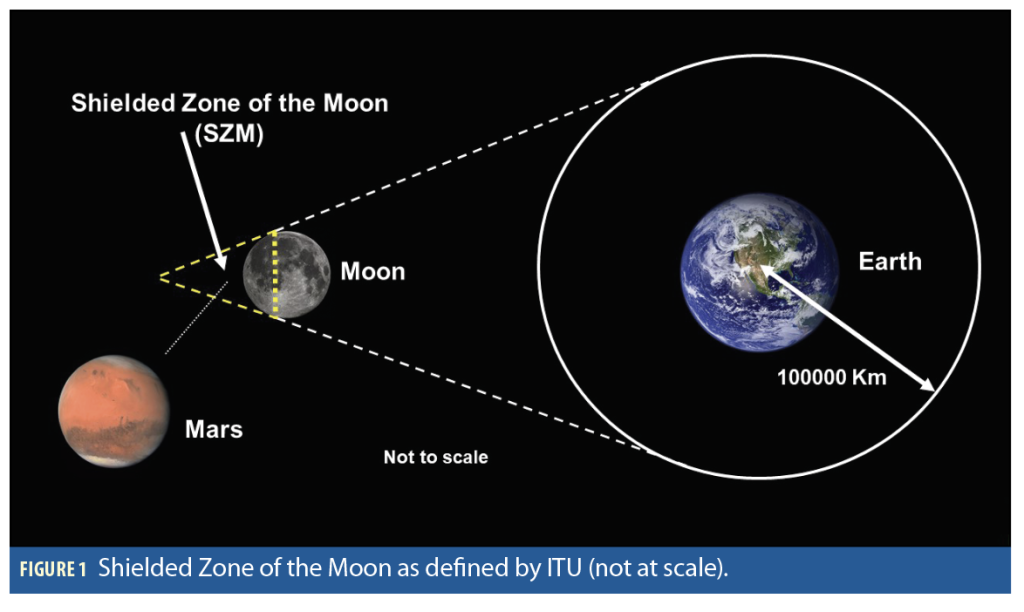

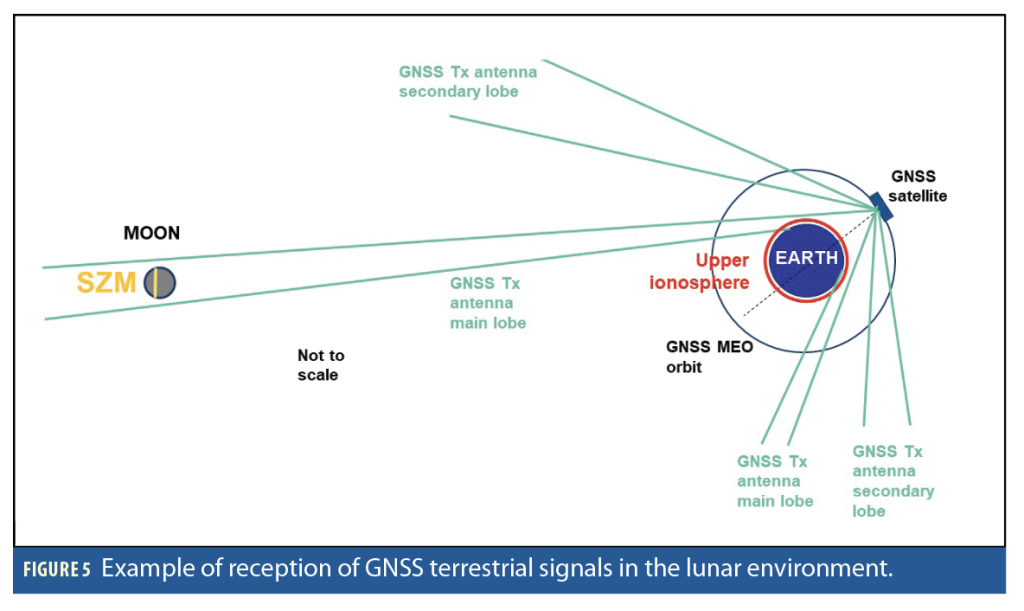
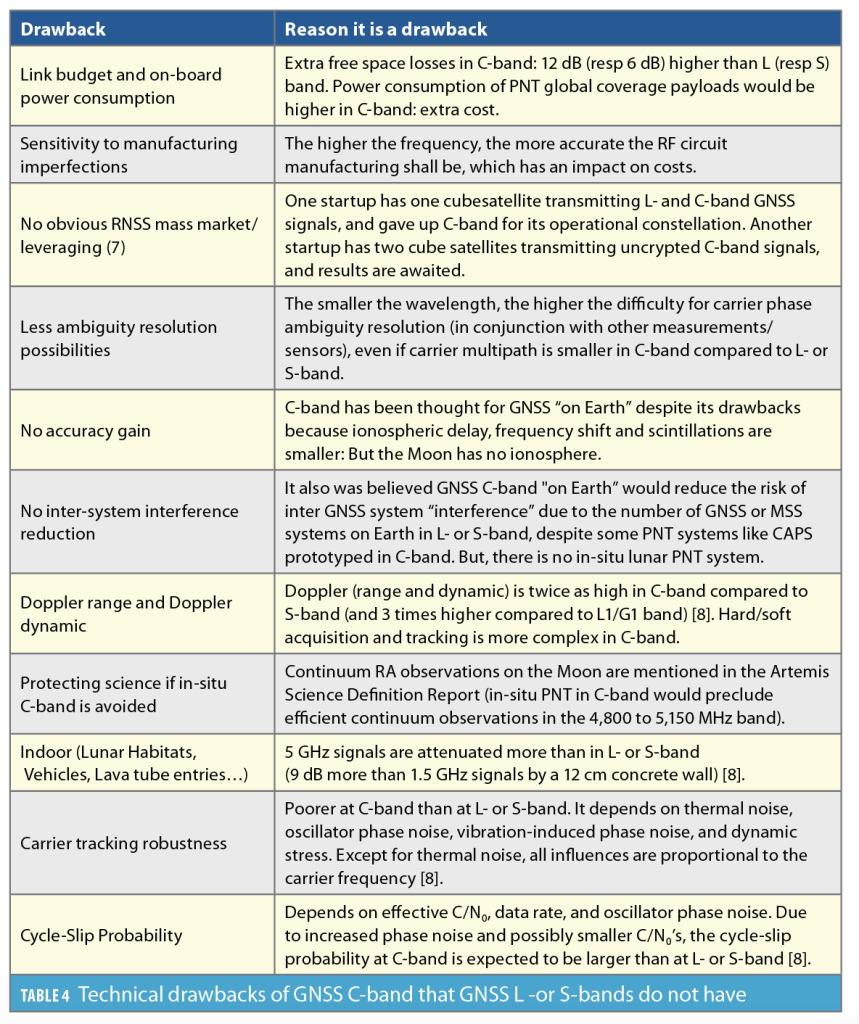
Protective measures: To protect RA in the SZM, stringent measures are required, including limiting radio transmissions in the SZM and ensuring that the lunar in-situ PNT system does not cause harmful interference to RA. This may involve power flux density (PFD) restrictions on PNT systems and protection of the C-band.
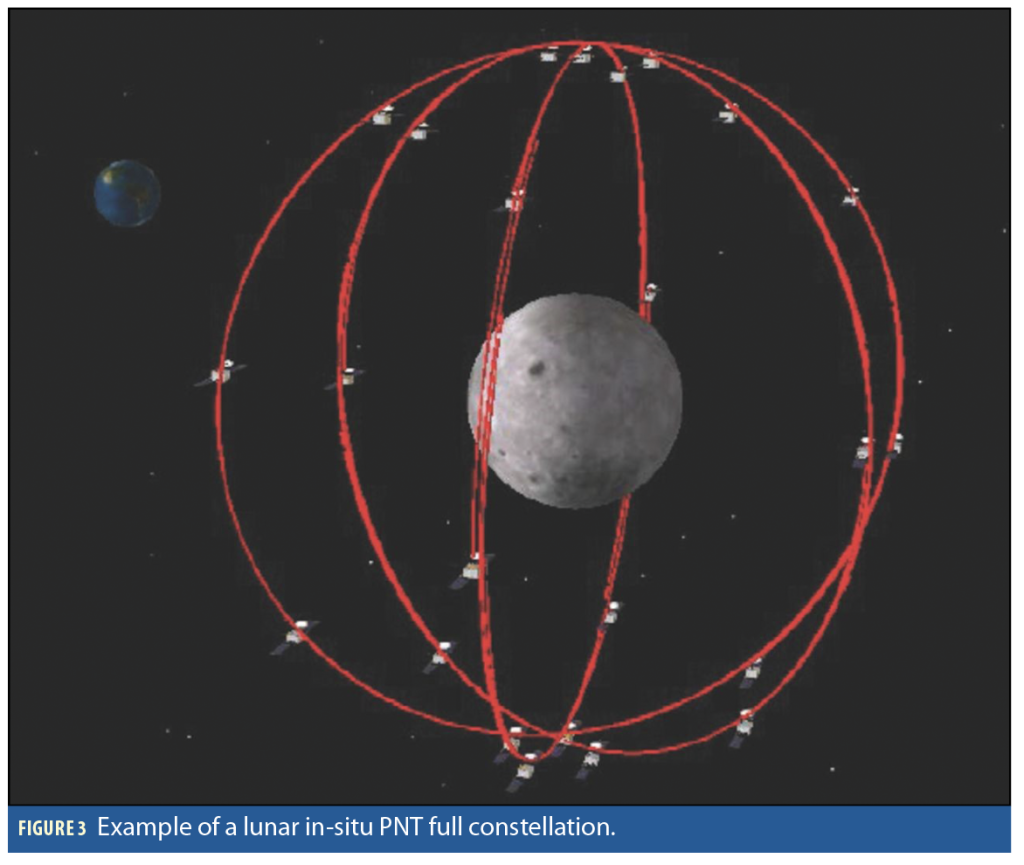
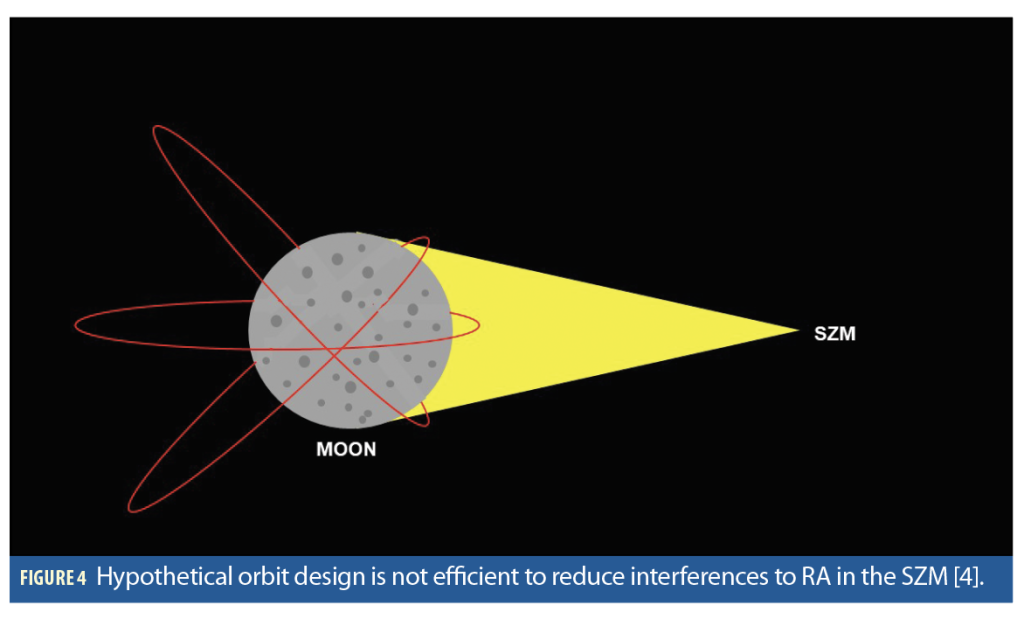
Sky-Earth Converged Networks: Sky-Earth Converged Networks have become an important trend in B5G and 6G communication networks as space and terrestrial networks converge. This kind of network can provide seamless global three-dimensional coverage and realise broadband mobile communications without blind zones, while supporting functions such as precise positioning, navigation and real-time Earth observation.
Applications of radio astronomy: Applications of radio astronomy include the use of radio telescopes and interferometers to observe celestial objects, which can penetrate the dust haze impenetrable to light waves and reveal radio images of celestial objects. Radio astronomy telescopes are also used to study solar activity and the surfaces of the planets in the solar system.
World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC): The WRC is an international conference that considers and decides on the use of the radio frequency spectrum and satellite orbits. the WRC's resolutions are essential for the development of the global radiocommunication service.
Septentrio Corporation and Septentrio Mosaic GNSS Modules: Septentrio is a company specialising in the design and manufacture of high-precision GNSS receivers for demanding applications requiring accuracy to the decimetre or centimetre level. septentrio's Mosaic series of GNSS modules, such as the mosaic- X5 and mosaic-T, provide full-constellation, multi-frequency, high-accuracy GNSS positioning that supports a wide range of current and future satellite signals. These modules have built-in AIM+, an advanced anti-jamming and anti-spoofing technology, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in challenging environments.