
Home This is the most straightforward method …

Configuring an inertial navigation product, especially as it relates to the setting of the alignment angle, is a critical step to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the system. Here are some basic steps and considerations:
Understand the alignment angle: the alignment angle is a critical parameter to ensure that the orientation of the inertial measurement unit (IMU) is aligned with the reference frame of the vehicle or application

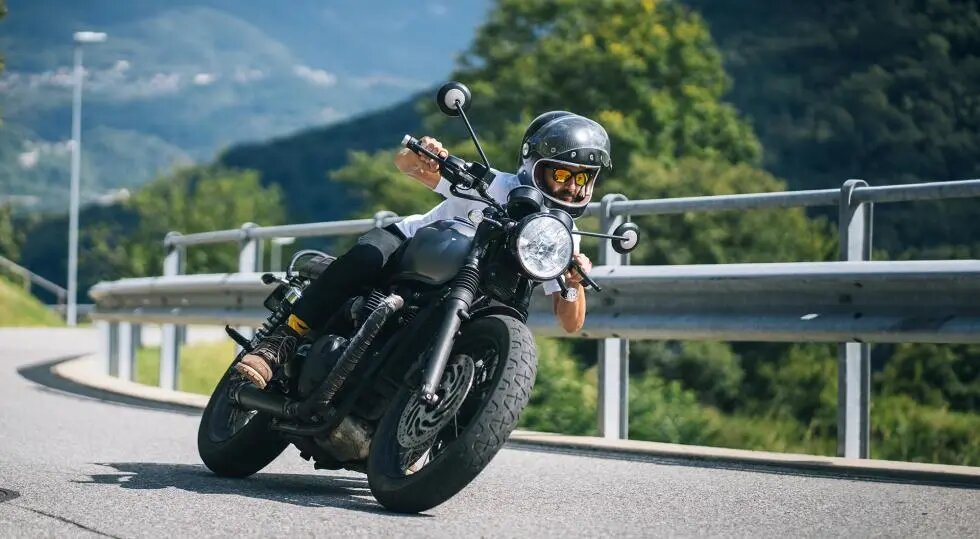
Two-wheeled vehicle applications: For two-wheeled vehicles, such as motorbikes or motor scooters, automatic alignment may not be applicable and therefore manual alignment must be performed. This is due to the fact that two-wheeled vehicles move with greater degrees of freedom and tilt angles, which complicates automatic alignment.

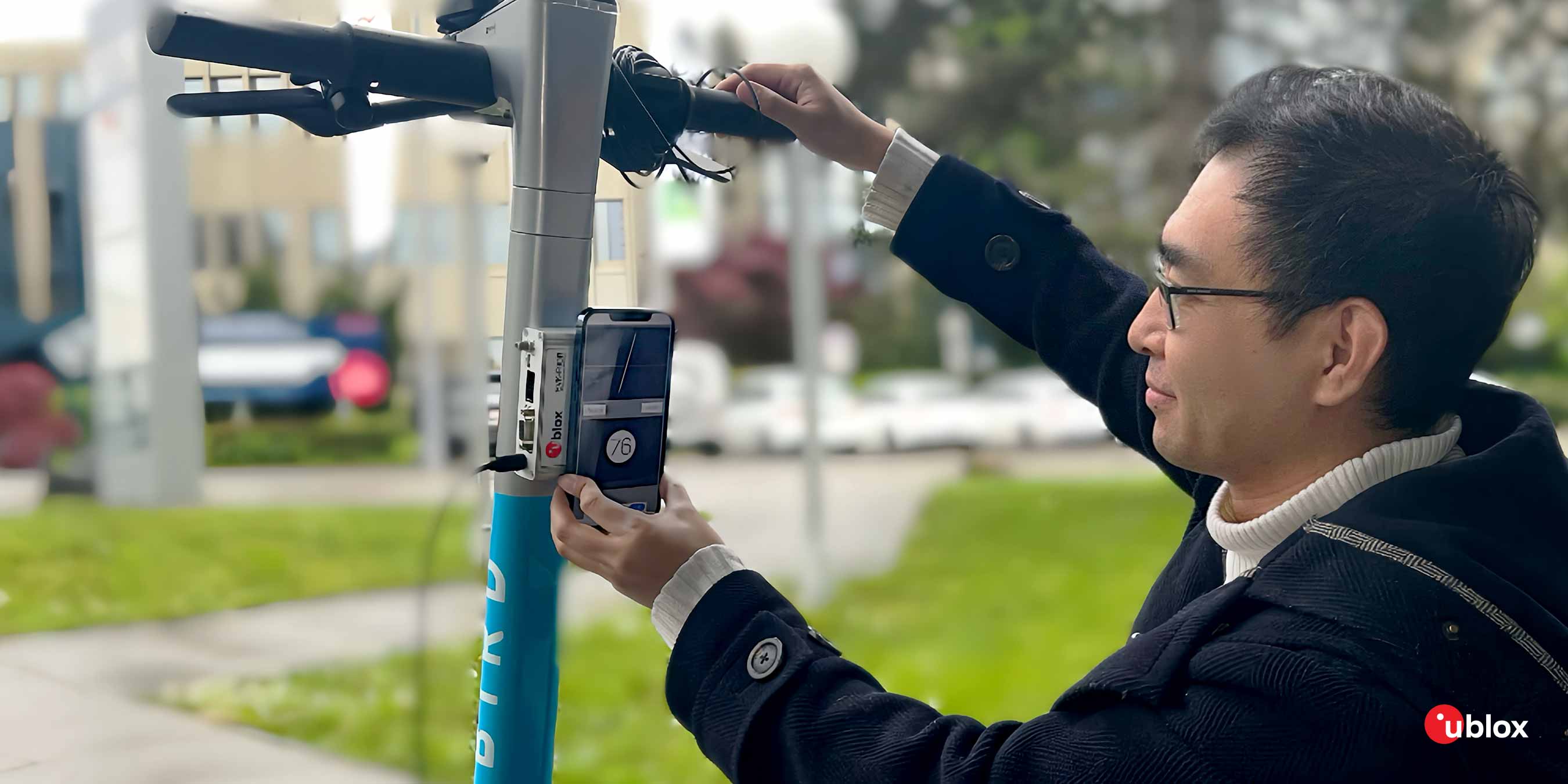
Error analysis: When designing and implementing the alignment process, it is important to understand and analyse the possible sources of error, including alignment errors in the IMU itself and errors introduced during installation.
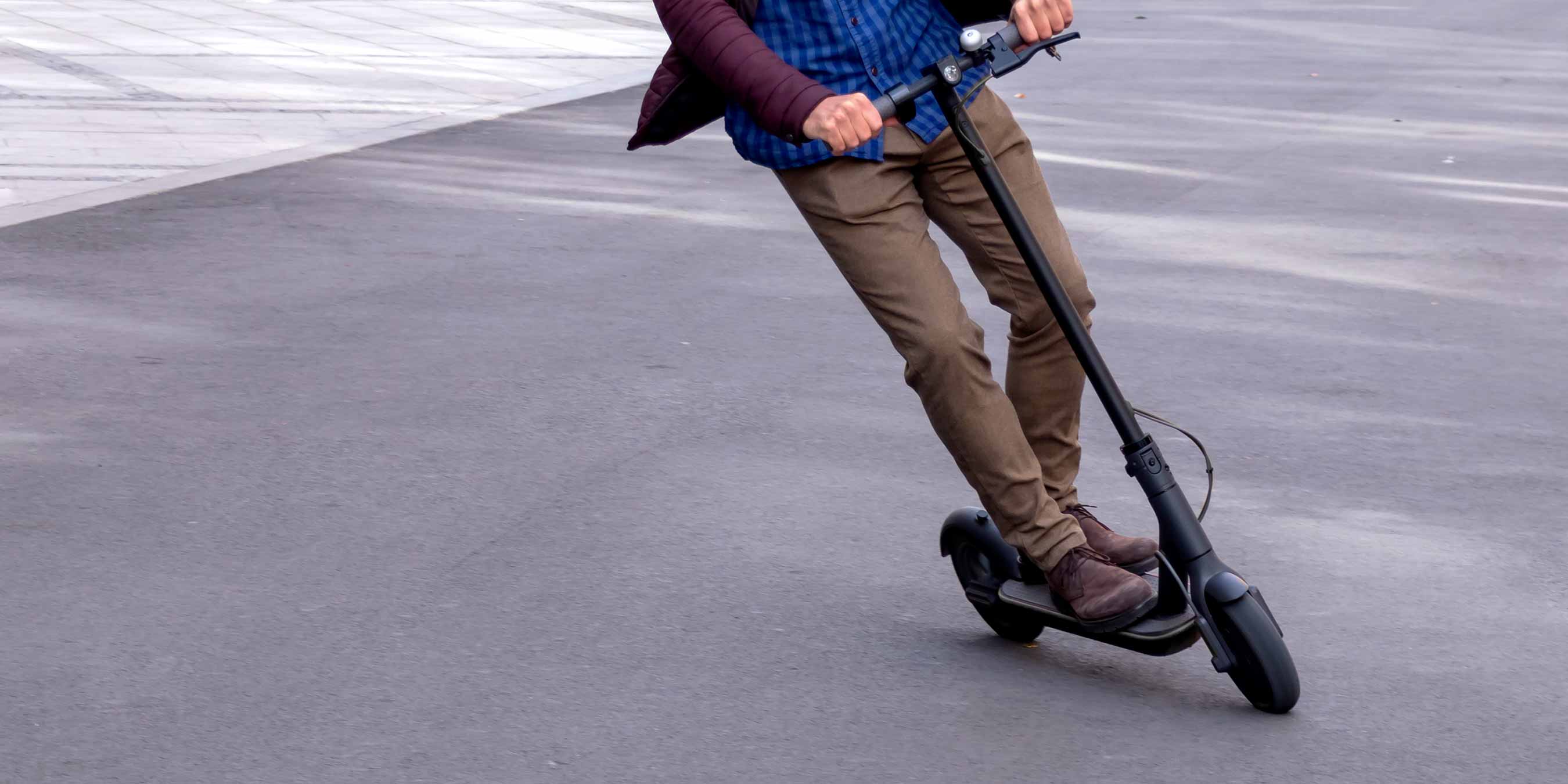
Electronic Alignment: If the IMU and mounting system cannot meet critical system objectives, alignment errors can be reduced through electronic alignment. This involves determining the alignment error term and applying a corrective alignment matrix.
Testing and validation: After the alignment process is complete, it is critical to conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure that the system is working as expected and providing the required accuracy.